IEC Releases Updated Standards for Insulator Tensile Testing: IEC 61089 & IEC 62219 Enhance Safety in Power Grid Infrastructure
Geneva, Switzerland – [Date] – The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has unveiled critical updates to its standards for tensile testing of overhead electrical insulators, with the publication of IEC 61089 and IEC 62219. These revisions aim to strengthen the reliability and safety of power transmission systems by refining testing protocols for insulators under horizontal tensile loads, a key factor in ensuring grid resilience amid escalating global energy demands.
Key Focus: Horizontal Tensile Testing Machines
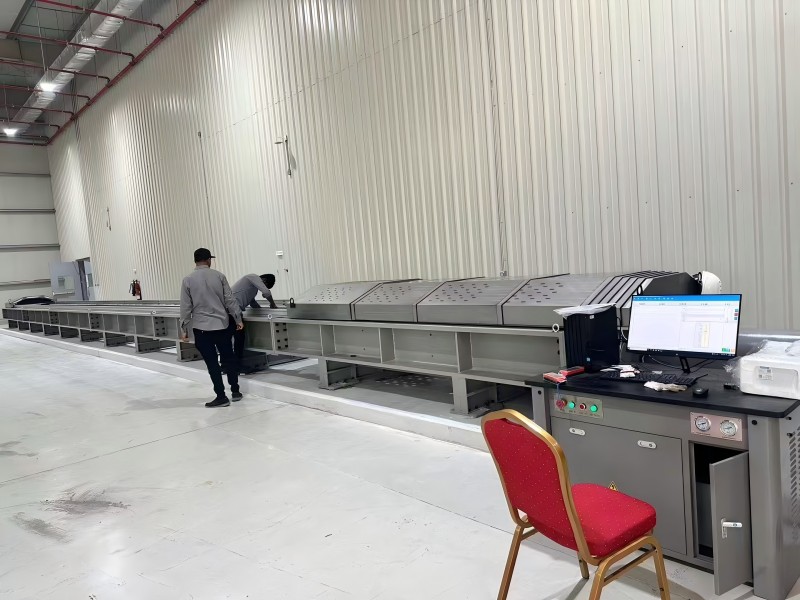
The updated standards emphasize the use of advanced horizontal tensile testing machines to simulate real-world mechanical stresses on insulators, including those caused by wind, ice accumulation, and conductor weight. Key parameters under scrutiny include:
- Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) of composite and ceramic insulators.
- Elongation at break and load-displacement behavior.
- Failure modes under prolonged stress cycles.
IEC 61089: This standard, applicable to round wire concentric lay overhead electrical stranded conductors, now integrates modern testing methodologies to address fatigue resistance and material degradation in harsh environments.
IEC 62219: Focused on composite insulators for overhead lines, the revised standard introduces stricter criteria for evaluating core-to-end-fitting adhesion and the long-term performance of polymeric materials.
Industry Impact
Power utilities and insulator manufacturers are expected to adopt these guidelines to comply with global safety benchmarks. Dr. Elena Müller, IEC Technical Committee Chair, stated, "These updates reflect decades of field data and advancements in material science. By standardizing horizontal tensile testing, we mitigate risks of insulator failure, which can lead to catastrophic grid outages."
Testing Process Highlights
- Sample Preparation: Insulators are mounted horizontally to replicate in-service orientation.
- Load Application: Gradual force increments until failure, with real-time monitoring of strain distribution.
- Data Analysis: Compliance is determined by comparing results against minimum UTS thresholds and deformation limits.
Global Adoption Timeline
The IEC recommends full implementation by Q3 2024, with certification bodies like UL and TÜV already updating audit frameworks. Major manufacturers, including Siemens Energy and Hubbell, have begun retrofitting testing facilities to meet the enhanced requirements.
Looking Ahead
The revisions align with the IEC’s broader mission to future-proof energy infrastructure against climate change and electrification challenges. Further collaboration with ISO and CIGRÉ is planned to harmonize testing standards across regions.